Jarrohlik mikroskoplarining neyroxirurgiyada qo'llanilishi va roli
Neyroxirurgiya tarixida qo'llanilishijarrohlik mikroskoplariyalang'och ko'z ostida jarrohlik amaliyotini o'tkazishning an'anaviy neyroxirurgik davridan zamonaviy neyroxirurgiya davriga ko'tarilgan yangi ramzdir.mikroskop. Kim va qachon qilganoperatsion mikroskoplarneyroxirurgiyada qo'llanila boshlandimi? Qanday roli borjarrohlik mikroskopneyroxirurgiya rivojlanishida o'ynagan? Fan va texnika taraqqiyoti bilan, irodaOperatsion mikroskopBa'zi ilg'or uskunalar bilan almashtirilishi mumkinmi? Bu har bir neyroxirurgning bilishi va neyroxirurgiya sohasidagi eng yangi texnologiya va asboblarni qo'llashi, neyroxirurgiya jarrohlik ko'nikmalarini takomillashtirishga yordam beradigan savol.
1, Tibbiyot sohasida mikroskopiyani qo'llash tarixi
Fizikada ko'zoynak linzalari - bu kattalashtiruvchi ta'sirga ega bo'lgan yagona tuzilishga ega bo'lgan konveks linzalari va ularning kattalashishi cheklangan, kattalashtiruvchi ko'zoynaklar deb nomlanadi. 1590 yilda ikki gollandiyalik nozik silindrsimon bochka ichiga ikkita qavariq linza plitasini o'rnatdi va shu bilan dunyodagi birinchi kompozitsion tuzilmani kattalashtiruvchi qurilmani ixtiro qildi:mikroskop. Keyinchalik mikroskopning tuzilishi doimiy ravishda takomillashtirildi va kattalashtirish doimiy ravishda oshdi. O'sha paytda olimlar bundan asosan foydalanganlarkompozit mikroskophayvonlar va o'simliklarning mayda tuzilmalarini, masalan, hujayralar tuzilishini kuzatish. 19-asrning oʻrtalari va oxirlaridan boshlab tibbiyot sohasida asta-sekin kattalashtiruvchi koʻzoynak va mikroskoplar qoʻllanila boshlandi. Dastlab, jarrohlar jarrohlik uchun burun ko'prigiga joylashtirilishi mumkin bo'lgan bitta linzali tuzilishga ega ko'zoynak uslubidagi kattalashtiruvchi ko'zoynaklardan foydalanganlar. 1876 yilda nemis shifokori Saemish dunyodagi birinchi "mikroskopik" operatsiyani murakkab ko'zoynakli kattalashtiruvchi oyna yordamida amalga oshirdi (jarrohlik turi noma'lum). 1893 yilda Germaniyaning Zeiss kompaniyasi ixtiro qildibinokulyar mikroskop, asosan tibbiy laboratoriyalarda eksperimental kuzatish uchun, shuningdek, oftalmologiya sohasida shox parda va old kameraning shikastlanishlarini kuzatish uchun ishlatiladi. 1921 yilda hayvonlarning ichki qulog'i anatomiyasi bo'yicha laboratoriya tadqiqotlariga asoslanib, shved otorinolaringologi Nylen fiksatordan foydalangan.monokulyar jarrohlik mikroskopodamlarda surunkali otit media operatsiyasini amalga oshirish uchun o'zi tomonidan ishlab chiqilgan va ishlab chiqarilgan, bu haqiqiy mikrojarrohlik edi. Bir yil o'tgach, Nylenning yuqori darajali shifokori Xlolmgren abinokulyar jarrohlik mikroskopoperatsiya xonasida Zeiss tomonidan ishlab chiqarilgan.
ErtaOperatsion mikroskoplarMexanik barqarorlikning yomonligi, harakatlanmaslik, turli o'qlarning yoritilishi va ob'ektiv linzalarning qizishi, tor jarrohlik kattalashtirish maydoni va boshqalar kabi ko'plab kamchiliklarga ega edi. Bularning barchasi kengroq qo'llanilishini cheklaydigan sabablardir.jarrohlik mikroskoplari. Keyingi o'ttiz yil ichida jarrohlar o'rtasidagi ijobiy o'zaro ta'sir tufayli vamikroskop ishlab chiqaruvchilari, ishlashijarrohlik mikroskoplaridoimiy ravishda takomillashtirildi vabinokulyar jarrohlik mikroskoplari, tomga o'rnatilgan mikroskoplar, zoom linzalari, koaksiyal yorug'lik manbai yoritilishi, elektron yoki suv bosimi bilan boshqariladigan bo'g'imli qo'llar, oyoq pedalini boshqarish va boshqalar ketma-ket ishlab chiqildi. 1953 yilda Germaniyaning Zeiss kompaniyasi bir qator ixtisoslashtirilgan mahsulotlarni ishlab chiqardiotologiya uchun jarrohlik mikroskoplar, ayniqsa, o'rta quloq va temporal suyak kabi chuqur jarohatlarda operatsiyalar uchun javob beradi. ning ijrosi davomidajarrohlik mikroskoplaritakomillashishda davom etmoqda, jarrohlarning fikrlash tarzi ham doimiy ravishda o'zgarib turadi. Masalan, nemis shifokorlari Zollner va Wullshteyn buni nazarda tutganjarrohlik mikroskoplaritimpanik membranani shakllantirish operatsiyasi uchun qo'llanilishi kerak. 1950-yillardan boshlab oftalmologlar oftalmologik tekshiruvlar uchun faqat mikroskoplardan foydalanish amaliyotini asta-sekin o'zgartirdilar va joriy etdilar.otoxirurgik mikroskoplaroftalmik jarrohlikda. O'shandan beri,Operatsion mikroskopotologiya va oftalmologiya sohalarida keng qo'llanilgan.
2, Neyroxirurgiyada jarrohlik mikroskopini qo'llash
Neyroxirurgiyaning o'ziga xosligi tufayli qo'llanilishineyroxirurgiyada jarrohlik mikroskoplariotologiya va oftalmologiyaga qaraganda biroz kechroqdir va neyroxirurglar ushbu yangi texnologiyani faol o'rganishmoqda. O'sha paytda,jarrohlik mikroskoplaridan foydalanishasosan Yevropada edi. Amerikalik oftalmolog Perrit birinchi marta tanishtirdijarrohlik mikroskoplari1946 yilda Yevropadan Qo'shma Shtatlarga amerikalik neyroxirurglar foydalanishi uchun poydevor qo'ydi.Operatsion mikroskoplar.
Inson hayotining qadr-qimmatini hurmat qilish nuqtai nazaridan, inson tanasi uchun ishlatiladigan har qanday yangi texnologiya, asbob-uskunalar yoki asboblar dastlabki hayvonlar tajribalari va operatorlar uchun texnik tayyorgarlikdan o'tishi kerak. 1955-yilda amerikalik neyroxirurg Malis hayvonlarda miya operatsiyasini o'tkazdibinokulyar jarrohlik mikroskop. Amerika Qo'shma Shtatlaridagi Janubiy Kaliforniya universitetining neyroxirurgi Kurze bir yil davomida mikroskop ostida quloq jarrohligini kuzatgandan so'ng laboratoriyada mikroskopdan foydalanishning jarrohlik usullarini o'rgandi. 1957 yil avgust oyida u 5 yoshli bolada akustik nevroma operatsiyasini muvaffaqiyatli amalga oshirdi.quloq jarrohlik mikroskop, bu dunyodagi birinchi mikrojarrohlik operatsiyasi edi. Ko'p o'tmay, Kurze bolaga yuz nervi sublingual nerv anastomozini muvaffaqiyatli amalga oshirdi.jarrohlik mikroskop, va bolaning tiklanishi juda yaxshi edi. Bu dunyodagi ikkinchi mikrojarrohlik operatsiyasi edi. Shundan so‘ng Kurze yuk mashinalarini olib yurganOperatsion mikroskoplarmikrojarrohlik neyroxirurgiyasi uchun turli joylarga va foydalanishni qat'iy tavsiya qildijarrohlik mikroskoplariboshqa neyroxirurglarga. Keyin Kurze miya anevrizmasini kesish operatsiyasini o'tkazdijarrohlik mikroskop(afsuski, u hech qanday maqola e'lon qilmagan). U 1961 yilda trigeminal nevralgiya bilan og'rigan bemorning ko'magida dunyodagi birinchi mikro bosh suyagiga asoslangan neyroxirurgiya laboratoriyasini yaratdi. Biz Kurzening mikroxirurgiyaga qo'shgan hissasini doimo yodda tutishimiz va uning yangi texnologiyalar va g'oyalarni qabul qilishdagi jasoratidan saboq olishimiz kerak. Biroq, 1990-yillarning boshlariga qadar, Xitoyda ba'zi neyroxirurglar qabul qilishmadiNeyroxirurgiya mikroskoplarijarrohlik uchun. Bu bilan muammo emas ediNeyroxirurgiya mikroskopio'zi, lekin neyroxirurglarning mafkuraviy tushunchasi bilan bog'liq muammo.
1958 yilda amerikalik neyroxirurg Donaghi Vermont shtatining Burlington shahrida dunyodagi birinchi mikroxirurgiya tadqiqot va o'quv laboratoriyasini tashkil qildi. Dastlabki bosqichlarda u o'z rahbarlari tomonidan chalkashlik va moliyaviy qiyinchiliklarga duch keldi. Akademiyada u doimo miya trombozi bo'lgan bemorlardan tromblarni to'g'ridan-to'g'ri olish uchun ochiq kortikal qon tomirlarini kesishni nazarda tutgan. Shunday qilib, u qon tomir jarroh Jeykobson bilan hayvonlar va klinik tadqiqotlar bo'yicha hamkorlik qildi. O'sha paytda, yalang'och ko'z sharoitida faqat diametri 7-8 millimetr va undan ko'p bo'lgan kichik qon tomirlarini tikish mumkin edi. Yupqa qon tomirlarining uchigacha anastomoziga erishish uchun Jeykobson birinchi marta ko'zoynak uslubidagi kattalashtiruvchi oynadan foydalanishga harakat qildi. Ko'p o'tmay, u foydalanishni esladiotorinolaringologiya jarrohlik mikroskoprezident shifokor bo'lganida jarrohlik uchun. Shunday qilib, Germaniyadagi Zeiss yordami bilan Jeykobson ikki operatorli jarrohlik mikroskopini yaratdi (Diploskop) tomir anastomozi uchun, bu ikki jarrohga bir vaqtning o'zida operatsiyani bajarishga imkon beradi. Hayvonlarda o'tkazilgan keng ko'lamli tajribalardan so'ng, Jeykobson qon tomir anastomozining 100% o'tkazuvchanligi bilan itlarning mikrojarrohlik anastomozi va karotid bo'lmagan arteriyalar (1960) haqida maqola chop etdi. Bu mikrojarrohlik neyroxirurgiyasi va qon tomir jarrohligi bilan bog'liq yangi tibbiy maqola. Jeykobson shuningdek, mikro qaychi, mikro igna ushlagichlar va mikro asboblar tutqichlari kabi ko'plab mikrojarrohlik asboblarini ishlab chiqdi. 1960 yilda Donaghi miya arteriyasini kesma trombektomiyasini muvaffaqiyatli amalga oshirdi.jarrohlik mikroskopmiya trombozi bilan og'rigan bemor uchun. Qo'shma Shtatlardan Rhoton 1967 yilda mikroskop ostida miya anatomiyasini o'rganishni boshladi, mikrojarrohlik anatomiyasining yangi sohasiga kashshof bo'ldi va mikrojarrohlik rivojiga katta hissa qo'shdi. ning afzalliklari tufaylijarrohlik mikroskoplariva mikrojarrohlik asboblarini takomillashtirish, tobora ko'proq jarrohlar foydalanishni yaxshi ko'radilarjarrohlik mikroskoplarijarrohlik uchun. Va mikrojarrohlik muolajalari bo'yicha ko'plab tegishli maqolalar chop etildi.
3, Xitoyda neyroxirurgiyada jarrohlik mikroskopini qo'llash
Yaponiyadagi vatanparvar xorijlik xitoylik sifatida professor Du Zivey birinchi mahalliy sovg'a qildineyroxirurgik mikroskopva tegishlimikrojarrohlik asboblari1972 yilda Suzhou tibbiyot kolleji filiali kasalxonasining neyroxirurgiya bo'limiga (hozirgi Suzhou universitetiga qarashli birinchi kasalxonaning neyroxirurgiya bo'limi). mavjudligi haqida bilib olgandan keyinneyroxirurgik mikroskoplarva mikrojarrohlik asboblari, Pekin Yivu kasalxonasining neyroxirurgiya bo'limi professori Chjao Yadu Suzhou tibbiyot kolleji professori Du Tsiveyga tashrif buyurdi.jarrohlik mikroskoplari. Shanxay Huashan kasalxonasidan professor Shi Yuquan mikrojarrohlik muolajalarini kuzatish uchun professor Du Tsiveyning bo‘limiga shaxsan tashrif buyurdi. Natijada, joriy etish, o'rganish va qo'llash to'lqiniNeyroxirurgiya mikroskoplariXitoyning yirik neyroxirurgiya markazlarida paydo bo'ldi, bu Xitoyning mikro neyroxirurgiyasining boshlanishini belgiladi.
4, Mikroxirurgiya jarrohlikning ta'siri
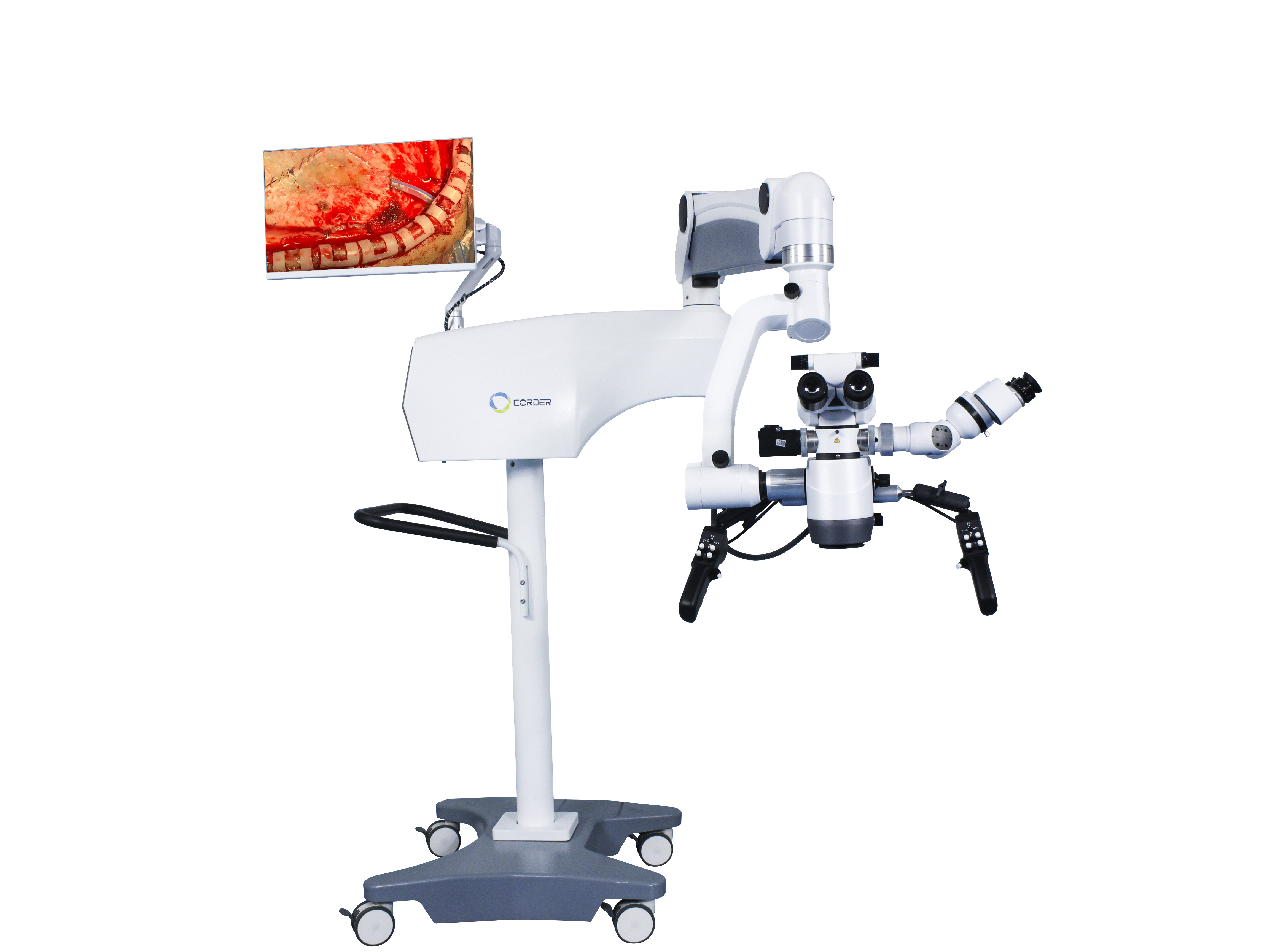
dan foydalanish tufaylineyroxirurgik mikroskoplar, yalang'och ko'z bilan amalga oshirib bo'lmaydigan operatsiyalar 6-10 marta kattalashtirish sharoitida amalga oshirilishi mumkin. Misol uchun, etmoid sinus orqali gipofiz o'smalari operatsiyasini bajarish normal gipofiz bezini himoya qilishda gipofiz o'smalarini xavfsiz aniqlash va olib tashlash mumkin; Yalang'och ko'z bilan amalga oshirib bo'lmaydigan jarrohlik, miya sopi o'smalari va orqa miya intramedullar o'smalari kabi yaxshiroq operatsiyalarga aylanishi mumkin. Akademik Vang Zhongcheng miya anevrizmasi operatsiyasidan oldin o'lim darajasi 10,7% ni tashkil etdi.neyroxirurgiya mikroskopi. 1978 yilda mikroskopdan foydalangandan so'ng, o'lim darajasi 3,2% gacha kamaydi. Miya arteriovenoz malformatsiyasini qo'llashsiz jarrohlikning o'lim darajasijarrohlik mikroskop6,2% ni tashkil etdi va 1984 yildan keyin a foydalanish bilanneyroxirurgiya mikroskoplari, o'lim darajasi 1,6% gacha kamaydi. dan foydalanishneyroxirurgiya mikroskopigipofiz o'smalarini kraniotomiyaga muhtoj bo'lmasdan minimal invaziv transnazal transsfenoidal yondashuv orqali davolashga imkon beradi, jarrohlik o'lim darajasini 4,7% dan 0,9% gacha kamaytiradi. Bu natijalarga erishish an'anaviy yalpi ko'z jarrohlik ostida mumkin emas, shuning uchunjarrohlik mikroskoplarizamonaviy neyroxirurgiya timsoli bo‘lib, zamonaviy neyroxirurgiyaning ajralmas va almashtirib bo‘lmaydigan jarrohlik asbob-uskunalaridan biriga aylandi.
Yuborilgan vaqt: 09-dekabr 2024-yil